Hello Guys !!
This is the one that covers the quantum mechanics and one of the most basics and will teach you about its model and tell about most basics and how many of its functions work.
This is basically being made up of basics energy and its shape as when we see how the electron is being placed.
These are mainly based on
1) de Broglie: This state that an electron follow both particle and wave nature and state that
(λ=h/ m * v)
2) Heisenberg Uncertainty: The basic Jist is that a particle both speed and position can not be detected Simultaneously.
3) Shrodinger: This can be easily be seen from my old post that is on the same topic. (LINK).
It is being describe by the help of
1)Principal energy level
2)Energy sublevel
3)Orbital (in each sublevel)
4)Spin
Principal Energy Level:- It is the shell number and represented by N
Energy Sublevel:- These have many other level known as S, P, D, F
Orbital:- Every energy sublevel has different spin and have them as
• s: 1 orbital
• p: 3 orbitals
• d: 5 orbitals
• f: 7 orbitals
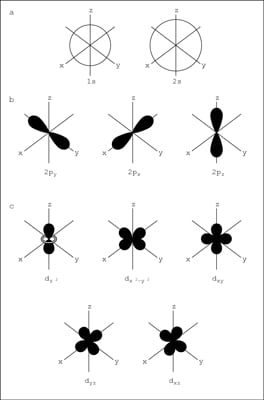
Spin:- Every orbital has two spin that is up and down.
There are mainly three rules that it follows
1. Aufbau principle: Each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available.
2. Pauli exclusion principle: A maximum of 2 electrons may occupy a single atomic orbital, but only if they have opposite spins.
3. Hund's rule: a single electron with the same spin must occupy each orbital in a sublevel before they pair up with an electron with an opposite spin.
This is the one that covers the quantum mechanics and one of the most basics and will teach you about its model and tell about most basics and how many of its functions work.
What is Quantum Mechanics Atomic Model
This is basically being made up of basics energy and its shape as when we see how the electron is being placed.
These are mainly based on
1) de Broglie: This state that an electron follow both particle and wave nature and state that
(λ=h/ m * v)
2) Heisenberg Uncertainty: The basic Jist is that a particle both speed and position can not be detected Simultaneously.
3) Shrodinger: This can be easily be seen from my old post that is on the same topic. (LINK).
It is being describe by the help of
1)Principal energy level
2)Energy sublevel
3)Orbital (in each sublevel)
4)Spin
Principal Energy Level:- It is the shell number and represented by N
Energy Sublevel:- These have many other level known as S, P, D, F
| Value of l (subshell) | Letter |
|---|---|
| 0 | s |
| 1 | p |
| 2 | d |
| 3 | f |
| 4 | g |
Orbital:- Every energy sublevel has different spin and have them as
• s: 1 orbital
• p: 3 orbitals
• d: 5 orbitals
• f: 7 orbitals

Spin:- Every orbital has two spin that is up and down.
Electronic Configuration
There are mainly three rules that it follows
1. Aufbau principle: Each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available.
2. Pauli exclusion principle: A maximum of 2 electrons may occupy a single atomic orbital, but only if they have opposite spins.
3. Hund's rule: a single electron with the same spin must occupy each orbital in a sublevel before they pair up with an electron with an opposite spin.
Electron Cloud
An electron cloud is the region of negative charge surrounding an atomic nucleus that is associated with an atomic orbital. It is defined mathematically, describing a region with a high probability of containing electrons.
The electron cloud model differs from the more simplistic Bohr model, in which electrons orbit the nucleus in much the same way as planets orbit the sun. In the cloud model, there are regions where an electron may likely be found, but it's theoretically possible for it to be located anywhere, including inside the nucleus.





No comments
Please comment here for suggestion and review